🏠 House Price Prediction - Regression & Classification Models
📹 Presentation Video
📋 Project Overview
This project predicts house prices using machine learning, implementing both regression (predicting exact price) and classification (predicting price category: Low/Medium/High) approaches.
Dataset
- Name: Global House Purchase Decision Dataset
- Size: 200,000 entries, 27 features
- Target: Property price prediction
Main Goals
- Predict house prices using regression models
- Classify properties into price categories (Low/Medium/High)
- Compare multiple ML algorithms and select the best performers
🔍 Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Price Distribution
Key Insights:
- Price distribution is slightly right-skewed
- Most properties fall in the low-to-medium price range
- Outliers exist in the high-price segment
Correlation Analysis
Key Findings:
- Property size has the strongest correlation with price
- Location features (country, city) significantly impact price
- Customer salary shows moderate correlation with purchase decisions
Feature Distributions
🛠️ Feature Engineering
New Features Created (9 total):
- property_age = 2025 - constructed_year
- rooms_to_bathrooms_ratio = rooms / (bathrooms + 1)
- total_amenities = garage + garden
- size_category = Small/Medium/Large bins
- safety_score = 1 / (crime_cases + legal_cases + 1)
- financial_capacity = customer_salary - monthly_expenses
- is_new_property = 1 if property_age <= 5
- high_satisfaction = 1 if satisfaction >= median
- location_quality = neighbourhood_rating + connectivity_score
One-Hot Encoding
- Encoded: country, city, property_type, furnishing_status, size_category
- Created ~60 binary columns
Polynomial Features
- property_size_sqft², customer_salary², property_age²
- Interaction terms (e.g., property_size × customer_salary)
Final Feature Count: 78 features
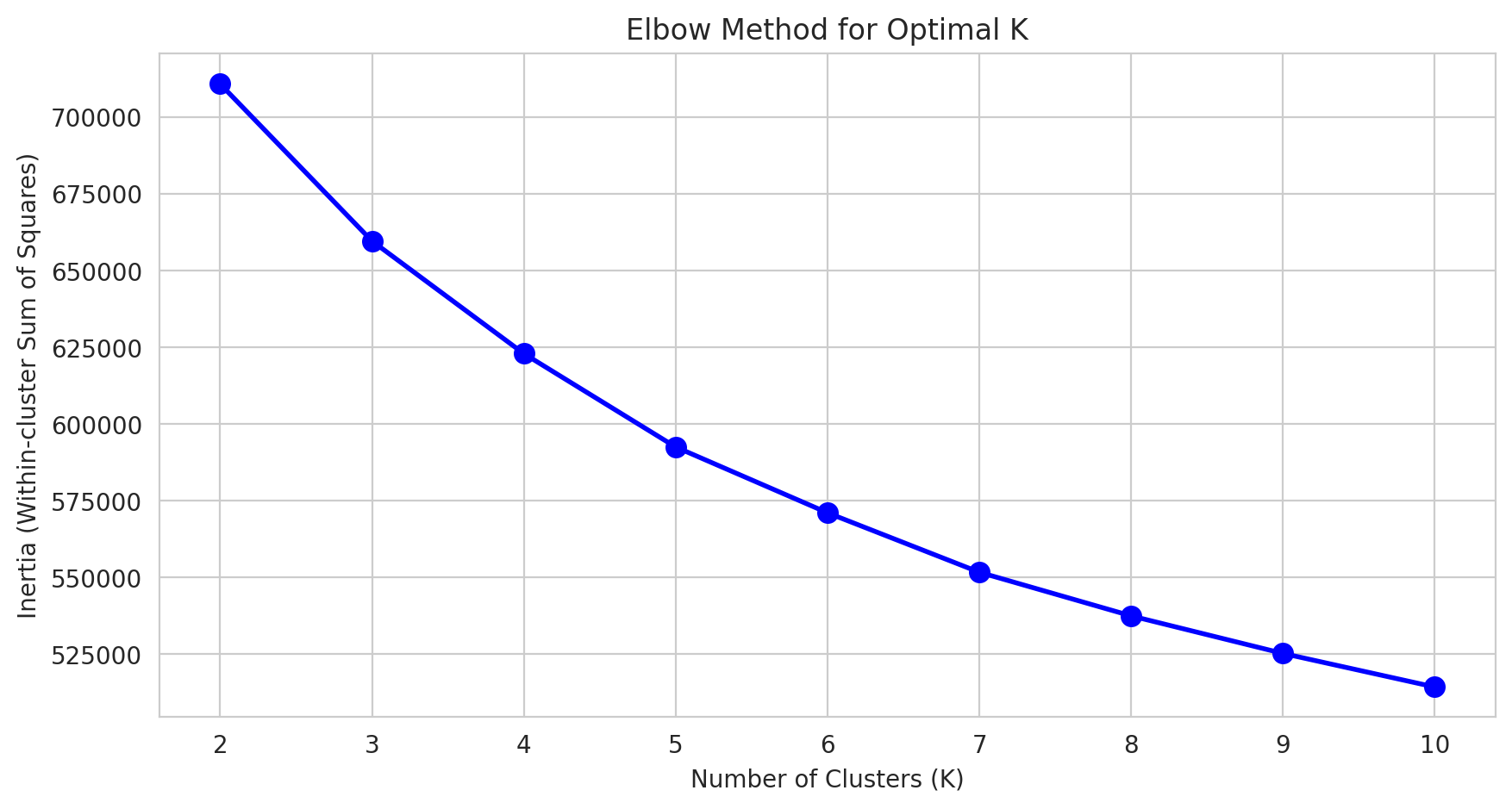
🎯 K-Means Clustering
Elbow Method for Optimal K
Selected K = 4 based on the elbow curve
Cluster Visualization (PCA)
Cluster Interpretation:
| Cluster | Property Age | Salary | Purchase Rate | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Older (50 yrs) | Low (~$29k) | 18% | Budget buyers, older properties |
| 1 | Older (33 yrs) | High (~$79k) | 22% | Affluent buyers |
| 2 | Newer (17 yrs) | Low (~$29k) | 18% | First-time buyers, new builds |
| 3 | Older (33 yrs) | Medium (~$50k) | 35% | Sweet spot - highest purchase rate |
📈 Part 1: Regression Models
Baseline Model (Linear Regression - Part 3)
- R²: 0.1945 (19.45%)
- MAE: 0.4168
- RMSE: 0.5345
Improved Models with Engineered Features (Part 5)
| Model | Train R² | Test R² | Test MAE | Test RMSE | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (Part 3) | 0.1919 | 0.1945 | 0.4168 | 0.5345 | - |
| Linear Regression | 0.9847 | 0.9845 | 0.0919 | 0.1237 | +406% |
| Random Forest | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 0.0054 | 0.0063 | +414% |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.9995 | 0.9994 | 0.0177 | 0.0236 | +414% |
Actual vs Predicted
Feature Importance
Top 5 Most Important Features (Random Forest):
- property_size_sqft × property_age (0.249)
- country_uae (0.197)
- country_usa (0.114)
- country_singapore (0.093)
- city_singapore (0.088)
🏆 Regression Winner: Random Forest
- Test R²: 0.9999 (99.99%)
- Test MAE: 0.0054
- Improvement: 414% over baseline
📊 Part 2: Classification Models
Target Conversion Strategy
Quantile Binning (3 Classes):
- Class 0 (Low): Price < 33rd percentile
- Class 1 (Medium): 33rd - 66th percentile
- Class 2 (High): Price ≥ 66th percentile
Class Distribution
| Class | Label | Count | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Low | 20,398 | 33.0% |
| 1 | Medium | 20,398 | 33.0% |
| 2 | High | 21,016 | 34.0% |
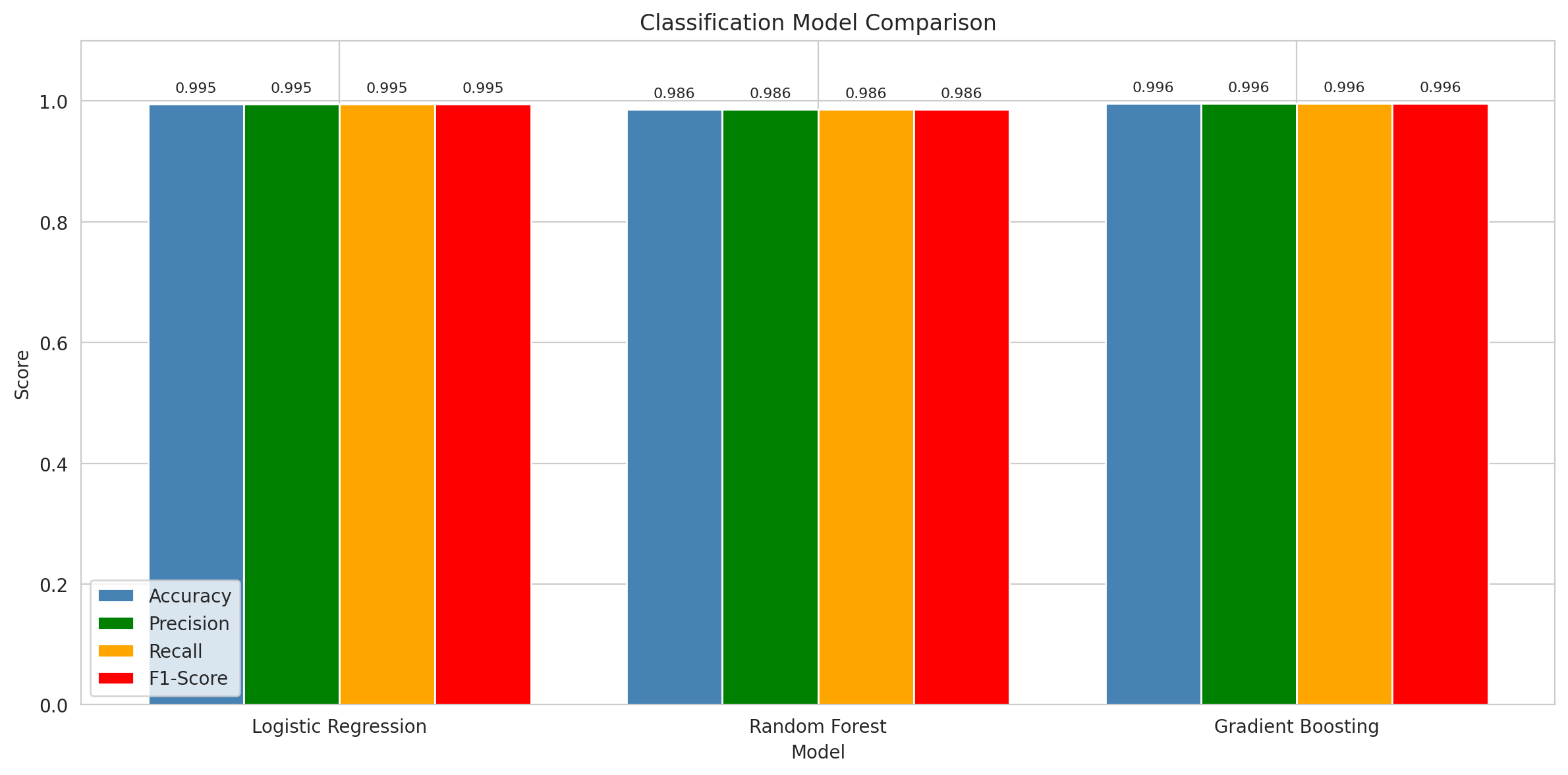
Model Performance
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 99.50% | 0.9949 | 0.9949 | 0.9949 |
| Random Forest | 98.58% | 0.9855 | 0.9855 | 0.9854 |
| Gradient Boosting | 99.56% | 0.9956 | 0.9956 | 0.9956 |
Confusion Matrices
🏆 Classification Winner: Gradient Boosting
- Accuracy: 99.56%
- F1-Score: 0.9956
- Total Errors: 55 out of 12,363 (0.44%)
🧠 Key Insights & Learnings
Precision vs Recall Analysis
- Precision is more important for house price classification
- False Positives (overvaluation) are more critical than False Negatives
- Overpricing can lead to: lost buyers, investor losses, legal issues
Challenges Faced
- Data Leakage: Initial model showed R² = 1.0 due to leaky features (loan_amount, down_payment). Removed them for valid results.
- Training Time: Gradient Boosting was slow; optimized hyperparameters for faster training.
- Feature Engineering: Creating meaningful features required domain knowledge about real estate.
Lessons Learned
- Always check for data leakage before trusting "perfect" results
- Feature engineering has massive impact (+400% improvement)
- Ensemble methods (Random Forest, Gradient Boosting) outperform linear models
- Location is the most important factor in house pricing
📁 Repository Contents
| File | Description |
|---|---|
random_forest_house_price_model.pkl |
Regression model (Random Forest) |
classification_model_winner.pkl |
Classification model (Gradient Boosting) |
house_purchase_dataset.csv |
Engineered dataset |
README.md |
This documentation |
🚀 Usage
Load Regression Model
import pickle
# Load model
with open('random_forest_house_price_model.pkl', 'rb') as f:
regression_model = pickle.load(f)
# Predict (features must be scaled and in same format as training)
predictions = regression_model.predict(X_scaled)
Load Classification Model
import pickle
# Load model
with open('classification_model_winner.pkl', 'rb') as f:
classification_model = pickle.load(f)
# Predict price class (0=Low, 1=Medium, 2=High)
price_class = classification_model.predict(X_scaled)
📊 Model Specifications
Regression Model (Random Forest)
Algorithm: RandomForestRegressor
n_estimators: 50
max_depth: 10
min_samples_split: 20
min_samples_leaf: 10
random_state: 42
Classification Model (Gradient Boosting)
Algorithm: GradientBoostingClassifier
n_estimators: 50
max_depth: 3
learning_rate: 0.2
subsample: 0.8
random_state: 42
👨💻 Author
Ethan Leor Gabis (ID: 209926781) Created as part of a Data Science course assignment.
📜 License
MIT License
- Downloads last month
- -
Inference Providers
NEW
This model isn't deployed by any Inference Provider.
🙋
Ask for provider support