Relational Visual Similarity --- Anonymous Captioning Model
 |
|---|
Thao Nguyen1, Sicheng Mo3, Krishna Kumar Singh2, Yilin Wang2, Jing Shi2, Nicholas Kolkin2, Eli Shechtman2, Yong Jae Lee1,2, ★, Yuheng Li1, ★
(★ Equal advising)
1- University of Wisconsin–Madison; 2- Adobe Research; 3- UCLA
TL;DR: We introduce a new visual similarity notion: relational visual similarity, which complements traditional attribute-based perceptual similarity (e.g., LPIPS, CLIP, DINO).
Click here to read Abstract 📝
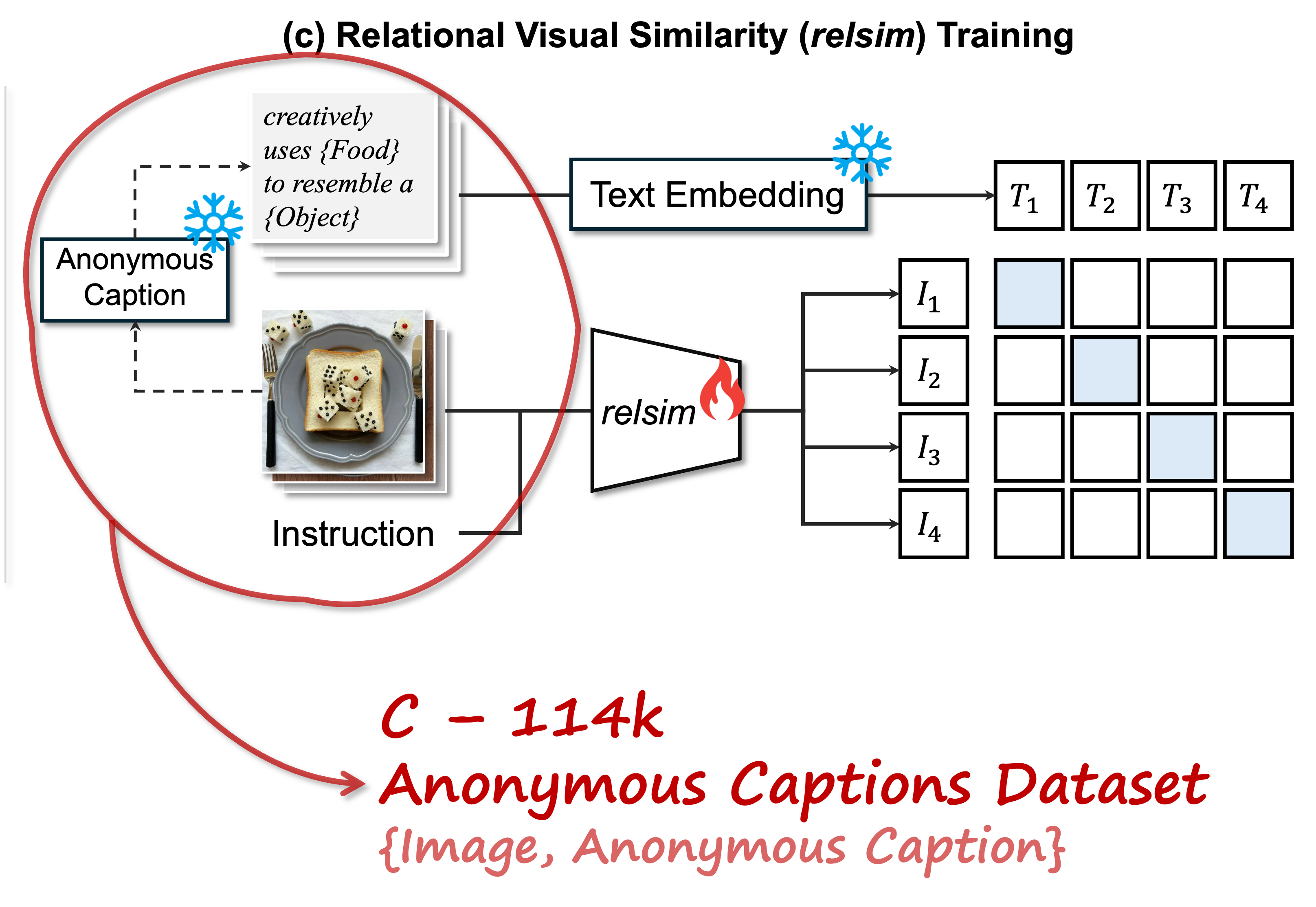
Humans do not just see attribute similarity---we also see relational similarity. An apple is like a peach because both are reddish fruit, but the Earth is also like a peach: its crust, mantle, and core correspond to the peach’s skin, flesh, and pit. This ability to perceive and recognize relational similarity, is arguable by cognitive scientist to be what distinguishes humans from other species. Yet, all widely used visual similarity metrics today (e.g., LPIPS, CLIP, DINO) focus solely on perceptual attribute similarity and fail to capture the rich, often surprising relational similarities that humans perceive. How can we go beyond the visible content of an image to capture its relational properties? How can we bring images with the same relational logic closer together in representation space? To answer these questions, we first formulate relational image similarity as a measurable problem: two images are relationally similar when their internal relations or functions among visual elements correspond, even if their visual attributes differ. We then curate 114k image–caption dataset in which the captions are anonymized---describing the underlying relational logic of the scene rather than its surface content. Using this dataset, we finetune a Vision–Language model to measure the relational similarity between images. This model serves as the first step toward connecting images by their underlying relational structure rather than their visible appearance. Our study shows that while relational similarity has a lot of real-world applications, existing image similarity models fail to capture it---revealing a critical gap in visual computing.Anonymous captions are image captions that do not refer to specific visible objects but instead capture the relational logic conveyed by the image.
You can use this anonymous captioning model as below:
import torch
from transformers import AutoProcessor, Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration
from peft import PeftModel
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
from PIL import Image
import requests
# Load model from HuggingFace
base_model = Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto"
)
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, "thaoshibe/relsim-anonymous-caption-qwen25vl-lora")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("thaoshibe/relsim-anonymous-caption-qwen25vl-lora", trust_remote_code=True)
# this is the test image
image_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/thaoshibe/relsim/refs/heads/main/anonymous_caption/mam2.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(image_url, stream=True).raw).convert("RGB").resize((448, 448))
####################################################
#
# Uncomment this and put your local image_path here
#
####################################################
# image = Image.open("imag_path").convert("RGB").resize((448, 448))
FIXED_PROMPT = '''
You are given a single image.
Carefully analyze it to understand its underlying logic, layout, structure, or creative concept. Then generate a single, reusable anonymous caption that could describe any image following the same concept.
The caption must:
- Fully capture the general logic or analogy of the image.
- Include placeholders (e.g., {Object}, {Word}, {Character}, {Meaning}, {Color}, etc.) wherever variations can occur.
- Be concise and standalone.
Important: Only output the anonymous caption. Do not provide any explanations or additional text.
'''
messages = [{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": FIXED_PROMPT}
]
}]
# Process and generate
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info([messages])
inputs = processor(text=[text], images=image_inputs, videos=video_inputs, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128, temperature=0.7, top_p=0.9)
caption = processor.decode(output[0][len(inputs.input_ids[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"Anonymous caption: {caption}")
The result of above code should be as follows:
| Input image | Generated anonymous captions (Different run) |
|---|---|
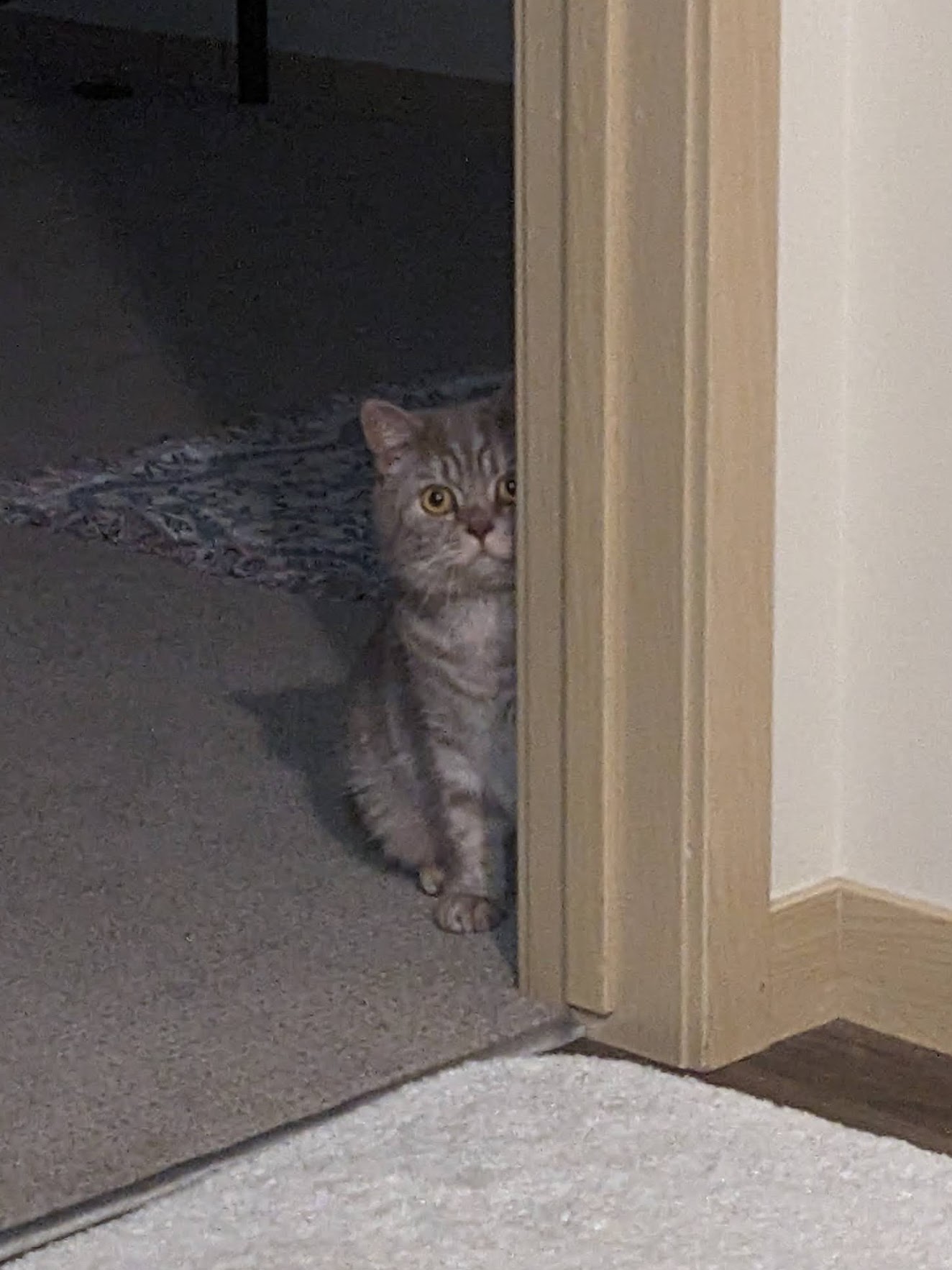 |
Example: python anonymous_caption/anonymous_caption.py --image_path anonymous_caption/mam.jpgRun 1: "Curious {Animal} peering out from behind a {Object}." Run 2: "Curious {Animal} peeking out from behind the {Object} in an unexpected and playful way." Run 3: "Curious {Cat} looking through a {Doorway} into the {Room}." Run 4: "A curious {Animal} peeking from behind a {Barrier}." Run 5: "A {Cat} peeking out from behind a {Door} with curious eyes." ... |
For more details, or training code, data, etc. Please visit: https://github.com/thaoshibe/relsim.
Thank you!!
Citation: arxiv.org/abs/2512.07833
@misc{nguyen2025relationalvisualsimilarity,
title={Relational Visual Similarity},
author={Thao Nguyen and Sicheng Mo and Krishna Kumar Singh and Yilin Wang and Jing Shi and Nicholas Kolkin and Eli Shechtman and Yong Jae Lee and Yuheng Li},
year={2025},
eprint={2512.07833},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.07833},
}
- Downloads last month
- 61
Model tree for thaoshibe/relsim-anonymous-caption-qwen25vl-lora
Base model
Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct





