BR - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on BR Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3 and 4)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics

Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8k | 3.122x | 3.07 | 0.4020% | 881,322 |
| 16k | 3.329x | 3.28 | 0.4286% | 826,606 |
| 32k | 3.492x | 3.44 | 0.4496% | 788,002 |
| 64k | 3.617x 🏆 | 3.56 | 0.4657% | 760,713 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: Fuentes de Jiloca zo ur gumun eus Spagn e Proviñs Zaragoza, en Aragon.
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁fu ent es ▁de ▁j il oc a ▁zo ▁ur ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 16k | ▁fu entes ▁de ▁j il oca ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ... (+8 more) |
18 |
| 32k | ▁fuentes ▁de ▁jil oca ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn ▁e ... (+6 more) |
16 |
| 64k | ▁fuentes ▁de ▁jil oca ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn ▁e ... (+6 more) |
16 |
Sample 2: `Barromán zo ur gumun eus Spagn, e proviñs Ávila, en Kastilha ha León.
Rummad:K...`
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁bar rom án ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
| 16k | ▁bar rom án ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
| 32k | ▁bar rom án ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
| 64k | ▁bar rom án ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
Sample 3: `Tolbaños zo ur gumun eus Spagn, e proviñs Ávila, en Kastilha ha León.
Rummad:K...`
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁tol b añ os ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ... (+15 more) |
25 |
| 16k | ▁tol b añ os ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ... (+15 more) |
25 |
| 32k | ▁tol b años ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
| 64k | ▁tol b años ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁eus ▁spagn , ▁e ... (+14 more) |
24 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 3.617x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.4020% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
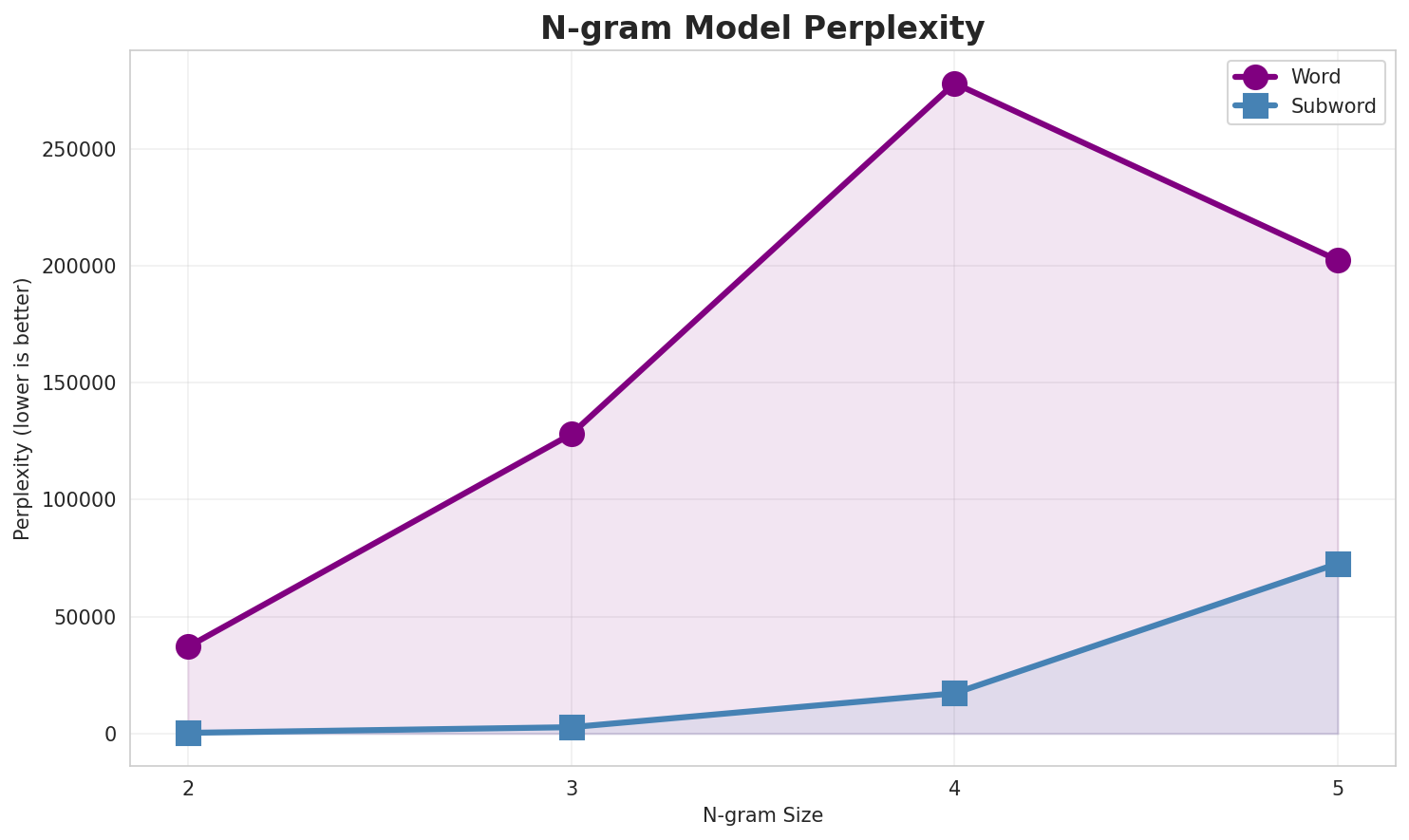
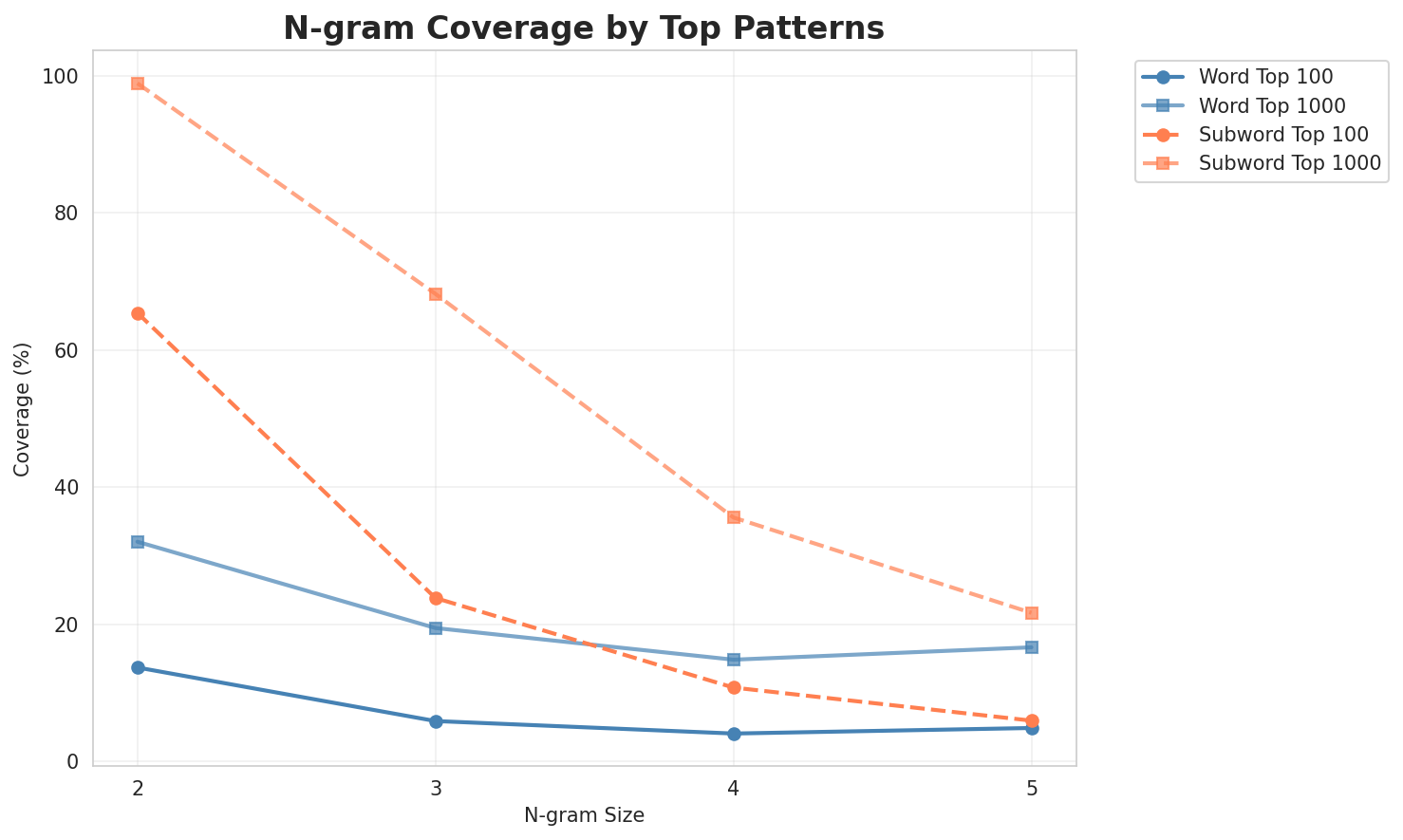
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
| N-gram | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | 37,795 🏆 | 15.21 | 396,301 | 15.5% | 32.7% |
| 2-gram | 361 🏆 | 8.49 | 13,774 | 60.5% | 98.2% |
| 3-gram | 147,885 | 17.17 | 858,386 | 7.1% | 19.7% |
| 3-gram | 3,461 | 11.76 | 106,981 | 21.9% | 63.7% |
| 4-gram | 382,971 | 18.55 | 1,581,104 | 3.6% | 13.2% |
| 4-gram | 22,182 | 14.44 | 580,225 | 10.3% | 33.1% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | c ' |
168,356 |
| 2 | rummad : |
166,928 |
| 3 | d ' |
113,851 |
| 4 | ' h |
99,333 |
| 5 | , e |
74,128 |
3-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ar c ' |
51,117 |
| 2 | d ' ar |
44,541 |
| 3 | d ' an |
33,579 |
| 4 | . rummad : |
24,562 |
| 5 | c ' hall |
23,162 |
4-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | bro - c ' |
16,536 |
| 2 | - c ' hall |
15,614 |
| 3 | zo ur gumun eus |
8,365 |
| 4 | ha daveennoù rummad : |
7,182 |
| 5 | notennoù ha daveennoù rummad |
7,173 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram with 361
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~33% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
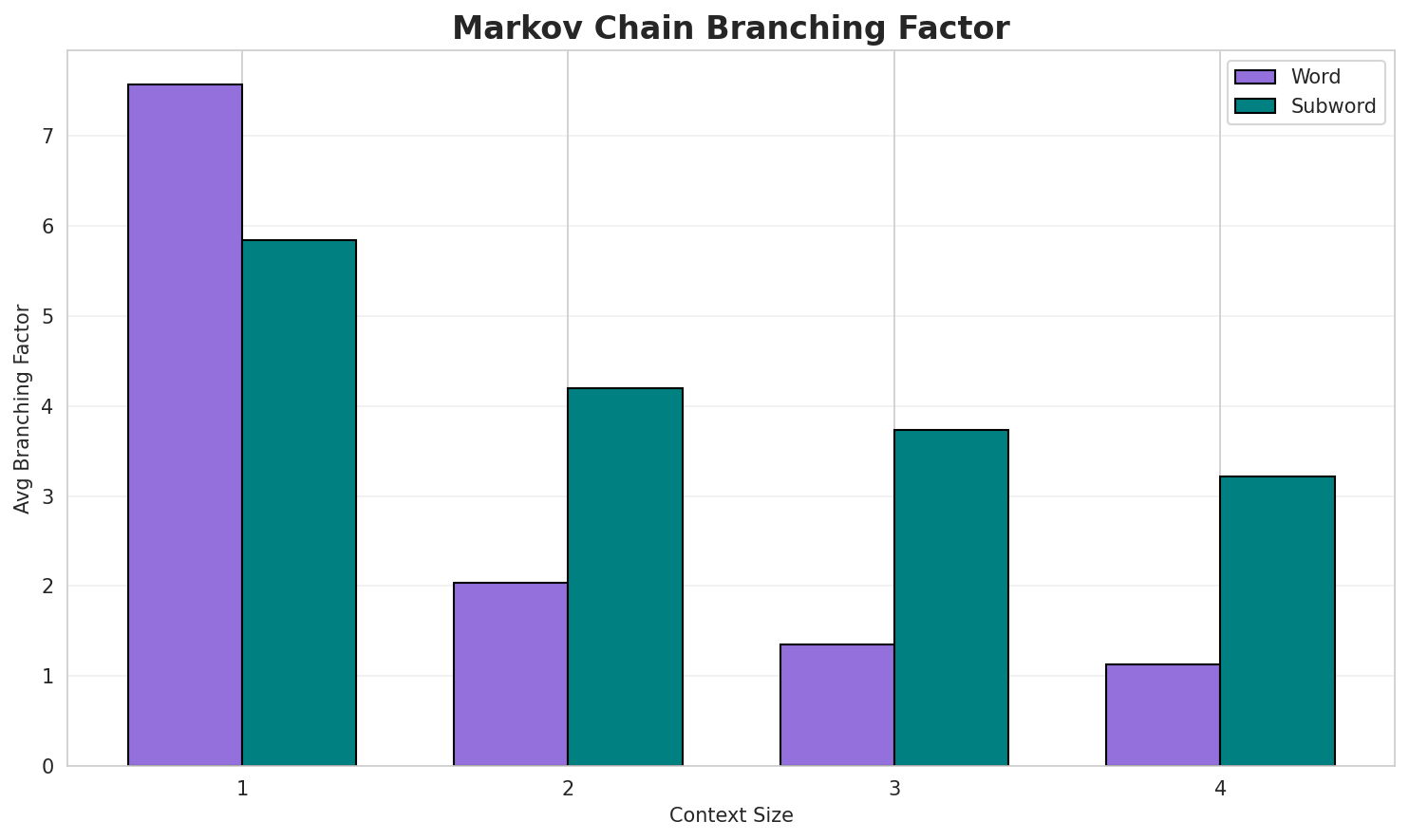
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
| Context | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.7133 | 1.640 | 6.37 | 642,948 | 28.7% |
| 1 | 1.1559 | 2.228 | 7.70 | 6,849 | 0.0% |
| 2 | 0.3934 | 1.313 | 2.35 | 4,087,653 | 60.7% |
| 2 | 0.7490 | 1.681 | 4.86 | 52,722 | 25.1% |
| 3 | 0.1872 | 1.139 | 1.44 | 9,600,283 | 81.3% |
| 3 | 0.7699 | 1.705 | 4.16 | 256,241 | 23.0% |
| 4 | 0.0950 🏆 | 1.068 | 1.19 | 13,824,129 | 90.5% |
| 4 | 0.6874 🏆 | 1.610 | 3.24 | 1,065,026 | 31.3% |
Generated Text Samples
Below are text samples generated from each Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
, job de reims . emañ o embann levrioù gant ur yezh romanek . ramsay ha- kreiz kalotenn skorn . sonet gantañ cheñch anv ar - se ne em gavas youenn. notennoù rummad : nobiliaire et tableaux d ' orgeraie ; barnet rust e - labour
Context Size 2:
c ' hommonwealth e beredoù ar brezel en ur bolz - enor e 1785 . darn allrummad : geomorfologiezh rummad : pladennoù brezhonek rummad : ganedigezhioù 1958 rummad : ganedigez...d ' ar gonfusianegezh lakaet e voe seitek nijour , ne c ' hoar vras paula (
Context Size 3:
ar c ' hentañ derez ) ofis publik ar brezhoneg . in : studia celtica18 / 19 :d ' ar 26 a viz eost . an anv implij al lerc ' h pa ' zd ' an arabegerion eta , evit skrivañ ar sañskriteg e vez implijet ar sistem - mañ gant
Context Size 4:
bro - c ' hall ) , e - lec ' h zo anvet pentre e kembre . hen- c ' hall ) d ' an 3 a viz genver 1871 . krouet e oa bet gantzo ur gumun eus italia , e proviñs cremona , e rannvro lombardia . rummad : kumunioù lombardia rumma...
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-4 with 90.5% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (1,065,026 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 263,085 |
| Total Tokens | 16,823,868 |
| Mean Frequency | 63.95 |
| Median Frequency | 4 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 2476.07 |
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | e | 717,291 |
| 2 | ar | 526,767 |
| 3 | a | 475,234 |
| 4 | an | 331,609 |
| 5 | ha | 233,395 |
| 6 | c | 194,241 |
| 7 | gant | 192,785 |
| 8 | en | 189,181 |
| 9 | da | 173,430 |
| 10 | rummad | 169,617 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | maghrebonkoud | 2 |
| 2 | fidefide | 2 |
| 3 | 2024he | 2 |
| 4 | ougandachess | 2 |
| 5 | ouganda365 | 2 |
| 6 | inmediares | 2 |
| 7 | cytonn | 2 |
| 8 | malinga | 2 |
| 9 | ablainville | 2 |
| 10 | remonter | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 1.1027 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.995216 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 40.0% |
| Top 1,000 | 64.0% |
| Top 5,000 | 79.7% |
| Top 10,000 | 85.1% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9952 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 40.0% of corpus
- Long Tail: 253,085 words needed for remaining 14.9% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
Model Comparison
| Model | Vocab Size | Dimension | Avg Norm | Std Norm | Isotropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 165,065 | 32 | 3.529 | 1.159 | 0.8322 🏆 |
| mono_64d | 165,065 | 64 | 4.045 | 1.139 | 0.8224 |
| mono_128d | 165,065 | 128 | 4.668 | 1.127 | 0.8005 |
| embeddings_enhanced | 0 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0000 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: mono_32d with 0.8322 (more uniform distribution)
- Dimension Trade-off: Higher dimensions capture more semantics but reduce isotropy
- Vocabulary Coverage: All models cover 165,065 words
- Recommendation: 100d for balanced semantic capture and efficiency
6. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 32k BPE | Best compression (3.62x) with low UNK rate |
| N-gram | 5-gram | Lowest perplexity (361) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (90.5%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
publisher = {HuggingFace},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2025-12-28 08:17:06