Udmurt - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on Udmurt Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4, 5-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions (aligned and unaligned)
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics
Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
- 7. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
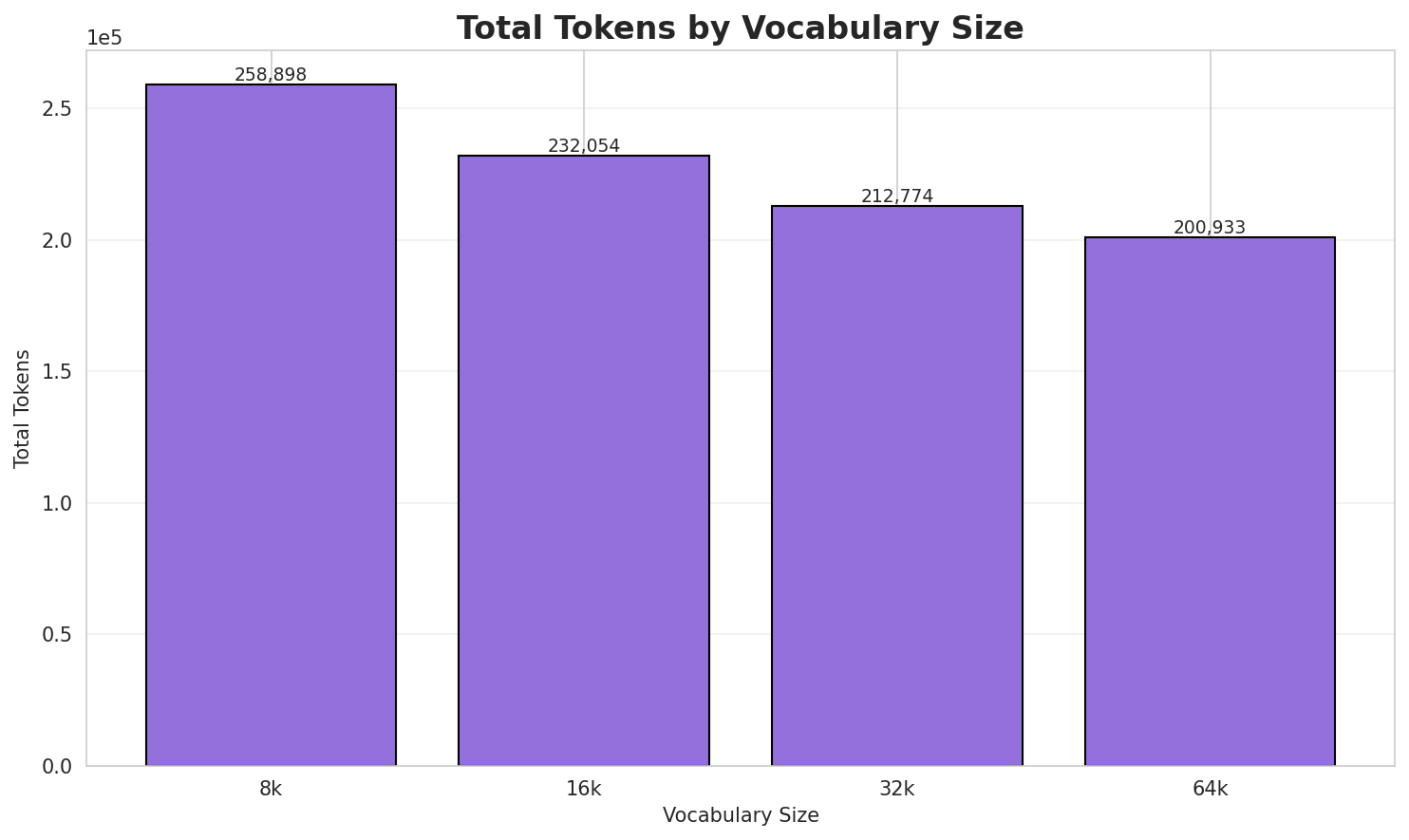
| 8k | 3.543x | 3.55 | 0.1375% | 258,898 |
| 16k | 3.952x | 3.96 | 0.1534% | 232,054 |
| 32k | 4.311x | 4.32 | 0.1673% | 212,774 |
| 64k | 4.565x 🏆 | 4.57 | 0.1772% | 200,933 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: Байраншур () — Удмуртиысь пичи шур. Бызе Яр ёрослэн музъеметӥз но усе Тум шуре. ...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁бай ран шур ▁() ▁— ▁удмуртиысь ▁пичи ▁шур . ▁бызе ... (+23 more) |
33 |
| 16k | ▁бай ран шур ▁() ▁— ▁удмуртиысь ▁пичи ▁шур . ▁бызе ... (+22 more) |
32 |
| 32k | ▁байран шур ▁() ▁— ▁удмуртиысь ▁пичи ▁шур . ▁бызе ▁яр ... (+20 more) |
30 |
| 64k | ▁байраншур ▁() ▁— ▁удмуртиысь ▁пичи ▁шур . ▁бызе ▁яр ▁ёрослэн ... (+19 more) |
29 |
Sample 2: Олеся Журакивська (; Киев, СССР, — Украин актриса. Фильмъёс Остров Донбас алфави...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁ол ес я ▁ж ур ак ив ська ▁(; ▁киев ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 16k | ▁ол ес я ▁ж ур ак ив ська ▁(; ▁киев ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 32k | ▁ол еся ▁жур акив ська ▁(; ▁киев , ▁ссср , ... (+9 more) |
19 |
| 64k | ▁ол еся ▁журакив ська ▁(; ▁киев , ▁ссср , ▁— ... (+8 more) |
18 |
Sample 3: Кривой Рог метротрам ( укр. Криворізький швидкісний трамвай )
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁кр ив ой ▁ро г ▁метро т рам ▁( ▁ук ... (+17 more) |
27 |
| 16k | ▁крив ой ▁рог ▁метро т рам ▁( ▁ук р . ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 32k | ▁крив ой ▁рог ▁метро трам ▁( ▁укр . ▁крив ор ... (+10 more) |
20 |
| 64k | ▁кривой ▁рог ▁метротрам ▁( ▁укр . ▁крив ор і зь ... (+5 more) |
15 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 4.565x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.1375% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
| N-gram | Variant | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | Word | 4,224 | 12.04 | 9,045 | 20.2% | 51.2% |
| 2-gram | Subword | 646 🏆 | 9.34 | 3,769 | 43.9% | 95.6% |
| 3-gram | Word | 4,567 | 12.16 | 10,317 | 20.4% | 49.5% |
| 3-gram | Subword | 5,398 | 12.40 | 30,259 | 15.9% | 50.6% |
| 4-gram | Word | 9,357 | 13.19 | 19,488 | 14.9% | 37.3% |
| 4-gram | Subword | 23,964 | 14.55 | 134,461 | 8.6% | 28.8% |
| 5-gram | Word | 7,868 | 12.94 | 14,631 | 14.0% | 37.7% |
| 5-gram | Subword | 56,525 | 15.79 | 261,817 | 5.4% | 21.0% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | j j |
743 |
| 2 | 1 тӥ |
662 |
| 3 | synonym of |
638 |
| 4 | now synonym |
606 |
| 5 | rchb f |
601 |
3-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | now synonym of |
604 |
| 2 | j j sm |
569 |
| 3 | ёросысь улон интыос |
559 |
| 4 | арын 1 тӥ |
533 |
| 5 | 1 тӥ толшоре |
490 |
4-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | арын 1 тӥ толшоре |
484 |
| 2 | улӥсьёс арын 1 тӥ |
482 |
| 3 | 1 тӥ толшоре гуртын |
478 |
| 4 | ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь |
414 |
| 5 | улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс |
414 |
5-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | улӥсьёс арын 1 тӥ толшоре |
482 |
| 2 | арын 1 тӥ толшоре гуртын |
478 |
| 3 | ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс |
414 |
| 4 | адями лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос |
404 |
| 5 | лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь |
396 |
2-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | н _ |
53,739 |
| 2 | . _ |
52,122 |
| 3 | с ь |
44,748 |
| 4 | _ к |
43,958 |
| 5 | , _ |
37,972 |
3-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | с ь _ |
23,826 |
| 2 | _ — _ |
21,444 |
| 3 | ы с ь |
19,313 |
| 4 | ъ ё с |
19,179 |
| 5 | ы н _ |
19,081 |
4-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ы с ь _ |
17,835 |
| 2 | л э н _ |
16,383 |
| 3 | _ н о _ |
10,521 |
| 4 | . _ — _ |
9,347 |
| 5 | ъ ё с _ |
7,031 |
5-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | у д м у р |
5,330 |
| 2 | д м у р т |
5,329 |
| 3 | _ у д м у |
4,783 |
| 4 | _ ё р о с |
4,592 |
| 5 | и ы с ь _ |
4,529 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram (subword) with 646
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~21% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
| Context | Variant | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
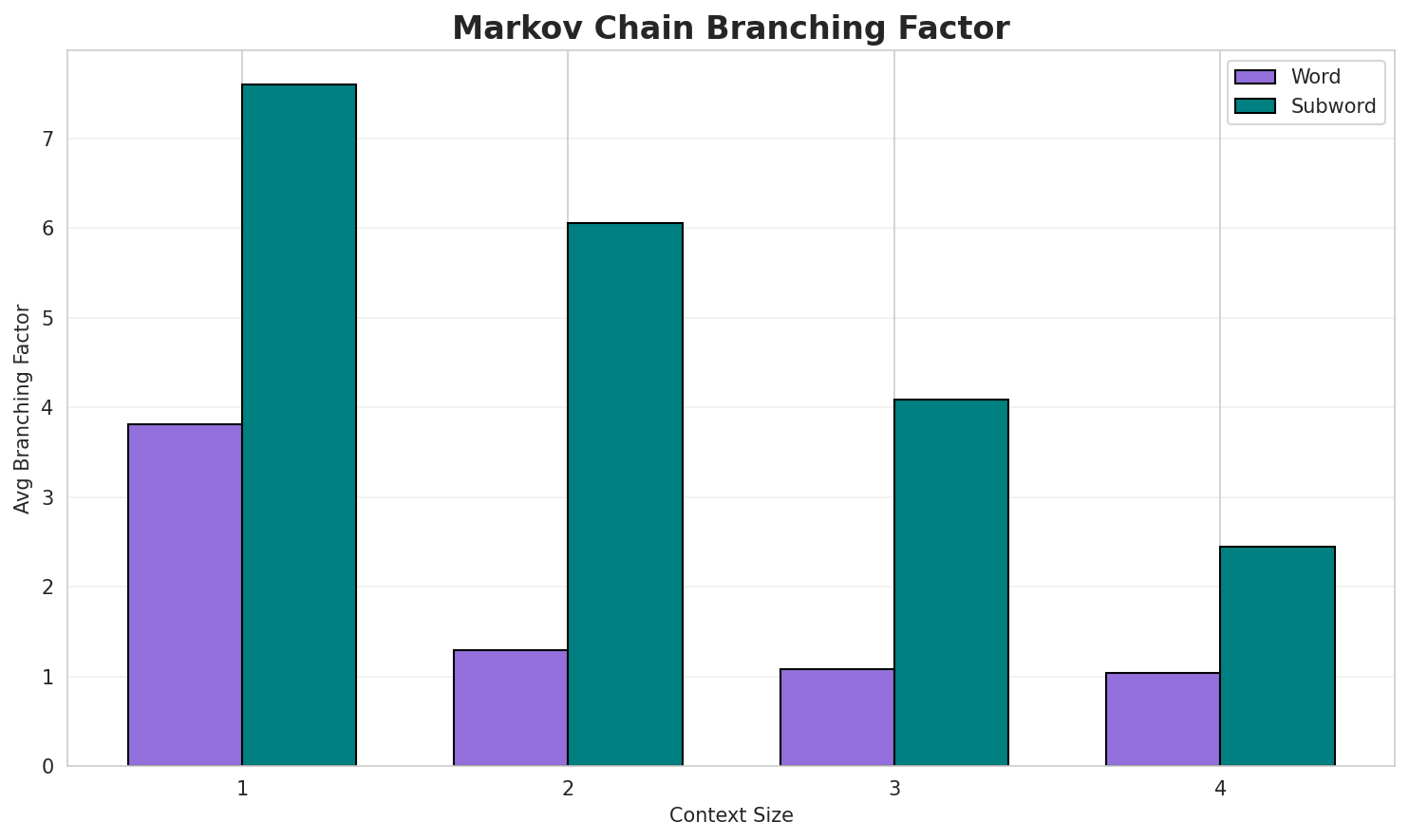
| 1 | Word | 0.6992 | 1.624 | 3.81 | 87,992 | 30.1% |
| 1 | Subword | 0.9862 | 1.981 | 7.60 | 1,200 | 1.4% |
| 2 | Word | 0.1500 | 1.110 | 1.29 | 333,544 | 85.0% |
| 2 | Subword | 0.9701 | 1.959 | 6.05 | 9,108 | 3.0% |
| 3 | Word | 0.0464 | 1.033 | 1.08 | 427,340 | 95.4% |
| 3 | Subword | 0.8614 | 1.817 | 4.08 | 55,078 | 13.9% |
| 4 | Word | 0.0213 🏆 | 1.015 | 1.04 | 457,825 | 97.9% |
| 4 | Subword | 0.5986 | 1.514 | 2.45 | 224,742 | 40.1% |
Generated Text Samples (Word-based)
Below are text samples generated from each word-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
но юскаре атаез агнешка но дунай мм пала адями лыдъяськиз пурга ёрослэн музъеметӥз шунды пуксён палл...арын 1 58 арын распределение бере кузон нефтеразведка участокъёс сад ёросын камбарка карын казахстан...тӥ мае пичи пургаысь сельлесхоз озьы ик сезьы кӧжы ӝук пӧзьто вӧсьсы бере баушев софин ӟуч
Context Size 2:
j j wood in j j sm ex koord schum galeola kuhlii rchb f hook f summerh1 тӥ толшоре гуртын 77 адями лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс улон интыоссы ёросысь ул...synonym of didactylus paradoxa luer dalström эквадор stelis nana lindl эквадор stelis pudens luer эк...
Context Size 3:
now synonym of crocodeilanthe cauliflora lindl luer pleurothallis pilostoma коста рика now synonym o...j j sm liparis cyperifolia ridl liparis dalessandroi dodson liparis dalzellii hook f liparis xanthin...арын 1 тӥ толшоре гуртын 378 адями лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс улон интыоссы
Context Size 4:
арын 1 тӥ толшоре гуртын 1 адями лыдъяськиз пурга ёросысь улон интыос пурга ёросысь гуртъёс улон инт...улӥсьёс арын 1 тӥ толшоре гуртын 82 адями лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс улон интыос...1 тӥ толшоре гуртын 43 адями лыдъяськиз ёросысь улон интыос ёросысь гуртъёс улон интыоссы
Generated Text Samples (Subword-based)
Below are text samples generated from each subword-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
_кеныст_чыни_._дай,_ктерспёсканысь._taccyncrs_ва
Context Size 2:
н_1-тӥсь_болос._e._—_вылэсовитич_(сь._—_aglowiedipt
Context Size 3:
сь_выль_венграв_мо_—_кость_садово_прысь_еврок_(hoehne_
Context Size 4:
ысь_улос,_кубикет_слэн_быдӟалаз_дӥсько_но_пичи_луыса._а._
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-4 (word) with 97.9% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (224,742 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 35,258 |
| Total Tokens | 485,306 |
| Mean Frequency | 13.76 |
| Median Frequency | 3 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 88.68 |
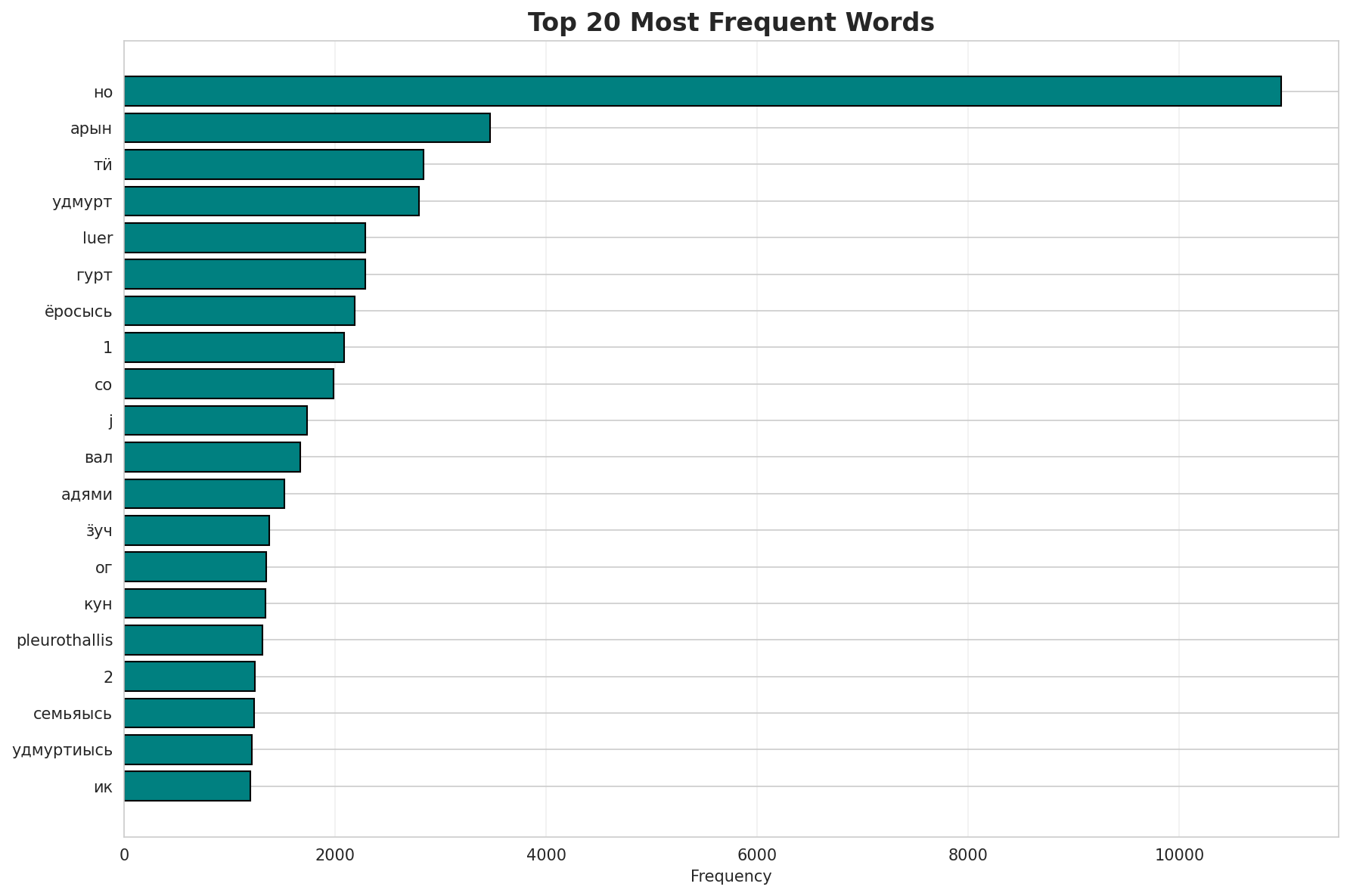
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | но | 10,962 |
| 2 | арын | 3,468 |
| 3 | тӥ | 2,839 |
| 4 | удмурт | 2,798 |
| 5 | luer | 2,289 |
| 6 | гурт | 2,284 |
| 7 | ёросысь | 2,189 |
| 8 | 1 | 2,085 |
| 9 | со | 1,987 |
| 10 | j | 1,734 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | телеграм | 2 |
| 2 | феминизмлы | 2 |
| 3 | вотчина | 2 |
| 4 | феминизм | 2 |
| 5 | глобалистъёслэн | 2 |
| 6 | пельмень | 2 |
| 7 | секта | 2 |
| 8 | версиозы | 2 |
| 9 | вераськет | 2 |
| 10 | эрис | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 1.0076 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.990825 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 22.1% |
| Top 1,000 | 54.2% |
| Top 5,000 | 76.3% |
| Top 10,000 | 85.1% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9908 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 22.1% of corpus
- Long Tail: 25,258 words needed for remaining 14.9% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
5.1 Cross-Lingual Alignment
5.2 Model Comparison
| Model | Dimension | Isotropy | Semantic Density | Alignment R@1 | Alignment R@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 32 | 0.6980 | 0.3482 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_64d | 64 | 0.4125 | 0.3188 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_128d | 128 | 0.0749 | 0.3189 | N/A | N/A |
| aligned_32d | 32 | 0.6980 🏆 | 0.3505 | 0.0080 | 0.1280 |
| aligned_64d | 64 | 0.4125 | 0.3252 | 0.0260 | 0.1660 |
| aligned_128d | 128 | 0.0749 | 0.3271 | 0.0420 | 0.1880 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: aligned_32d with 0.6980 (more uniform distribution)
- Semantic Density: Average pairwise similarity of 0.3314. Lower values indicate better semantic separation.
- Alignment Quality: Aligned models achieve up to 4.2% R@1 in cross-lingual retrieval.
- Recommendation: 128d aligned for best cross-lingual performance
6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
This section presents an automated morphological analysis derived from the statistical divergence between word-level and subword-level models. By analyzing where subword predictability spikes and where word-level coverage fails, we can infer linguistic structures without supervised data.
6.1 Productivity & Complexity
| Metric | Value | Interpretation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Productivity Index | 5.000 | High morphological productivity | Reliable analysis |
| Idiomaticity Gap | 0.793 | High formulaic/idiomatic content | - |
6.2 Affix Inventory (Productive Units)
These are the most productive prefixes and suffixes identified by sampling the vocabulary for global substitutability patterns. A unit is considered an affix if stripping it leaves a valid stem that appears in other contexts.
Productive Prefixes
| Prefix | Examples |
|---|---|
-к |
кит, кубоказ, косметической |
-с |
списокезлэн, серем, сюрреализм |
-п |
петра, прокурорез, пӧйшурало |
-в |
выжонни, выжыысьтызы, валаз |
-б |
берлинэ, бавариысь, борок |
-а |
алжирлэн, австрия, александрович |
-м |
мазунинской, механик, мозмытӥсь |
-т |
театральная, теориен, талибъёслы |
Productive Suffixes
| Suffix | Examples |
|---|---|
-н |
алжирлэн, гвинеяын, набережнойын |
-эн |
алжирлэн, цехезлэн, ельцинлэн |
-a |
parvula, michelia, glaucophylla |
-з |
валаз, кубоказ, прокурорез |
-сь |
бавариысь, мозмытӥсь, дэремлэсь |
-ь |
бавариысь, мозмытӥсь, дэремлэсь |
-ын |
гвинеяын, набережнойын, европаын |
-ы |
выжыысьтызы, ӝутӥськизы, шудӥсьлы |
6.3 Bound Stems (Lexical Roots)
Bound stems are high-frequency subword units that are semantically cohesive but rarely appear as standalone words. These often correspond to the 'core' of a word that requires inflection or derivation to be valid.
| Stem | Cohesion | Substitutability | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
иськ |
1.61x | 95 contexts | иськем, миськон, иськеме |
anth |
2.47x | 18 contexts | euanthe, panther, anthrax |
тъёс |
1.67x | 59 contexts | юртъёс, кутъёс, катъёс |
тэмы |
2.15x | 22 contexts | итэмын, актэмыр, ватэмын |
ръёс |
1.52x | 81 contexts | ӧръёс, аръёс, шуръёс |
тӥсь |
1.61x | 61 contexts | кутӥсь, чутӥсь, потӥсь |
эмын |
2.07x | 23 contexts | улэмын, алэмын, луэмын |
ъёсы |
1.46x | 83 contexts | ожъёсы, аръёсы, ужъёсыз |
ской |
2.07x | 20 contexts | чудской, рижской, вотской |
нъёс |
1.70x | 39 contexts | дунъёс, вынъёс, синъёс |
яськ |
1.57x | 28 contexts | сяська, сяськае, сяськая |
емын |
1.71x | 18 contexts | ваемын, ошемын, утемын |
6.4 Affix Compatibility (Co-occurrence)
This table shows which prefixes and suffixes most frequently co-occur on the same stems, revealing the 'stacking' rules of the language's morphology.
| Prefix | Suffix | Frequency | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
-к |
-н |
157 words | кубертен, кудымкарын |
-т |
-н |
71 words | тропинин, трактэн |
-п |
-н |
70 words | петровичлэн, план |
-к |
-з |
70 words | катэныз, коллегиез |
-к |
-ы |
64 words | кивалтӥсезлы, кузьымлы |
-п |
-з |
64 words | пыронэз, палозяз |
-к |
-эн |
64 words | кивалтэтэзлэн, калыкъёслэн |
-с |
-н |
63 words | суданлэн, спринтын |
-в |
-н |
61 words | валамон, валтӥсьёсызлэн |
-г |
-н |
53 words | героезлэн, гербезлэн |
6.5 Recursive Morpheme Segmentation
Using Recursive Hierarchical Substitutability, we decompose complex words into their constituent morphemes. This approach handles nested affixes (e.g., prefix-prefix-root-suffix).
| Word | Suggested Split | Confidence | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|
| комитетсы | комитет-с-ы |
7.5 | с |
| факультетсэ | факультет-с-э |
7.5 | с |
| процентысь | процент-ы-сь |
6.0 | процент |
| ссылкаысь | ссылка-ы-сь |
6.0 | ссылка |
| шормуӵысь | шормуӵ-ы-сь |
6.0 | шормуӵ |
| школаослы | школа-ос-лы |
6.0 | школа |
| группаослы | группа-ос-лы |
6.0 | группа |
| историысь | истори-ы-сь |
6.0 | истори |
| округъёсы | округъёс-ы |
4.5 | округъёс |
| планетаос | планета-ос |
4.5 | планета |
| журналистикая | журналистика-я |
4.5 | журналистика |
| системаын | система-ын |
4.5 | система |
| куартолэзен | куартолэзе-н |
4.5 | куартолэзе |
| возьматон | возьмато-н |
4.5 | возьмато |
| разделъёсыз | разделъёс-ыз |
4.5 | разделъёс |
6.6 Linguistic Interpretation
Automated Insight: The language Udmurt shows high morphological productivity. The subword models are significantly more efficient than word models, suggesting a rich system of affixation or compounding.
Note on Idiomaticity: The high Idiomaticity Gap suggests a large number of frequent multi-word expressions or formulaic sequences that are statistically distinct from their component parts.
7. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 64k BPE | Best compression (4.56x) |
| N-gram | 2-gram | Lowest perplexity (646) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (97.9%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.18073153},
publisher = {Zenodo},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
- 🤝 Sponsor: Featherless AI
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2026-01-11 02:18:53