language: br
language_name: Breton
language_family: celtic_brythonic
tags:
- wikilangs
- nlp
- tokenizer
- embeddings
- n-gram
- markov
- wikipedia
- feature-extraction
- sentence-similarity
- tokenization
- n-grams
- markov-chain
- text-mining
- fasttext
- babelvec
- vocabulous
- vocabulary
- monolingual
- family-celtic_brythonic
license: mit
library_name: wikilangs
pipeline_tag: text-generation
datasets:
- omarkamali/wikipedia-monthly
dataset_info:
name: wikipedia-monthly
description: Monthly snapshots of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages
metrics:
- name: best_compression_ratio
type: compression
value: 3.787
- name: best_isotropy
type: isotropy
value: 0.8154
- name: vocabulary_size
type: vocab
value: 0
generated: 2026-01-03T00:00:00.000Z
Breton - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on Breton Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4, 5-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions (aligned and unaligned)
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics
Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
- 7. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8k | 3.238x | 3.24 | 0.4518% | 788,643 |
| 16k | 3.463x | 3.46 | 0.4832% | 737,391 |
| 32k | 3.647x | 3.65 | 0.5089% | 700,148 |
| 64k | 3.787x 🏆 | 3.79 | 0.5284% | 674,255 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: Concetta Barra a oa ur ganerez hag un aktourez italian ha dreist-holl napolitane...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁conc etta ▁bar ra ▁a ▁oa ▁ur ▁ganerez ▁hag ▁un ... (+30 more) |
40 |
| 16k | ▁conc etta ▁barra ▁a ▁oa ▁ur ▁ganerez ▁hag ▁un ▁aktourez ... (+26 more) |
36 |
| 32k | ▁conc etta ▁barra ▁a ▁oa ▁ur ▁ganerez ▁hag ▁un ▁aktourez ... (+26 more) |
36 |
| 64k | ▁conc etta ▁barra ▁a ▁oa ▁ur ▁ganerez ▁hag ▁un ▁aktourez ... (+22 more) |
32 |
Sample 2: Fénis zo ur gumun italian, e rannvro emren Traoñienn Aosta. Notennoù
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁f én is ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁italian , ▁e ▁rannvro ... (+6 more) |
16 |
| 16k | ▁f én is ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁italian , ▁e ▁rannvro ... (+5 more) |
15 |
| 32k | ▁f én is ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁italian , ▁e ▁rannvro ... (+5 more) |
15 |
| 64k | ▁fén is ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁italian , ▁e ▁rannvro ▁emren ... (+4 more) |
14 |
Sample 3: Cervera del Río Alhama zo ur gumun e kumuniezh emren La Rioja e Spagn.
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁c erv era ▁del ▁río ▁al h ama ▁zo ▁ur ... (+9 more) |
19 |
| 16k | ▁cerv era ▁del ▁río ▁al h ama ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ... (+8 more) |
18 |
| 32k | ▁cerv era ▁del ▁río ▁al h ama ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ... (+8 more) |
18 |
| 64k | ▁cervera ▁del ▁río ▁alhama ▁zo ▁ur ▁gumun ▁e ▁kumuniezh ▁emren ... (+5 more) |
15 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 3.787x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.4518% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
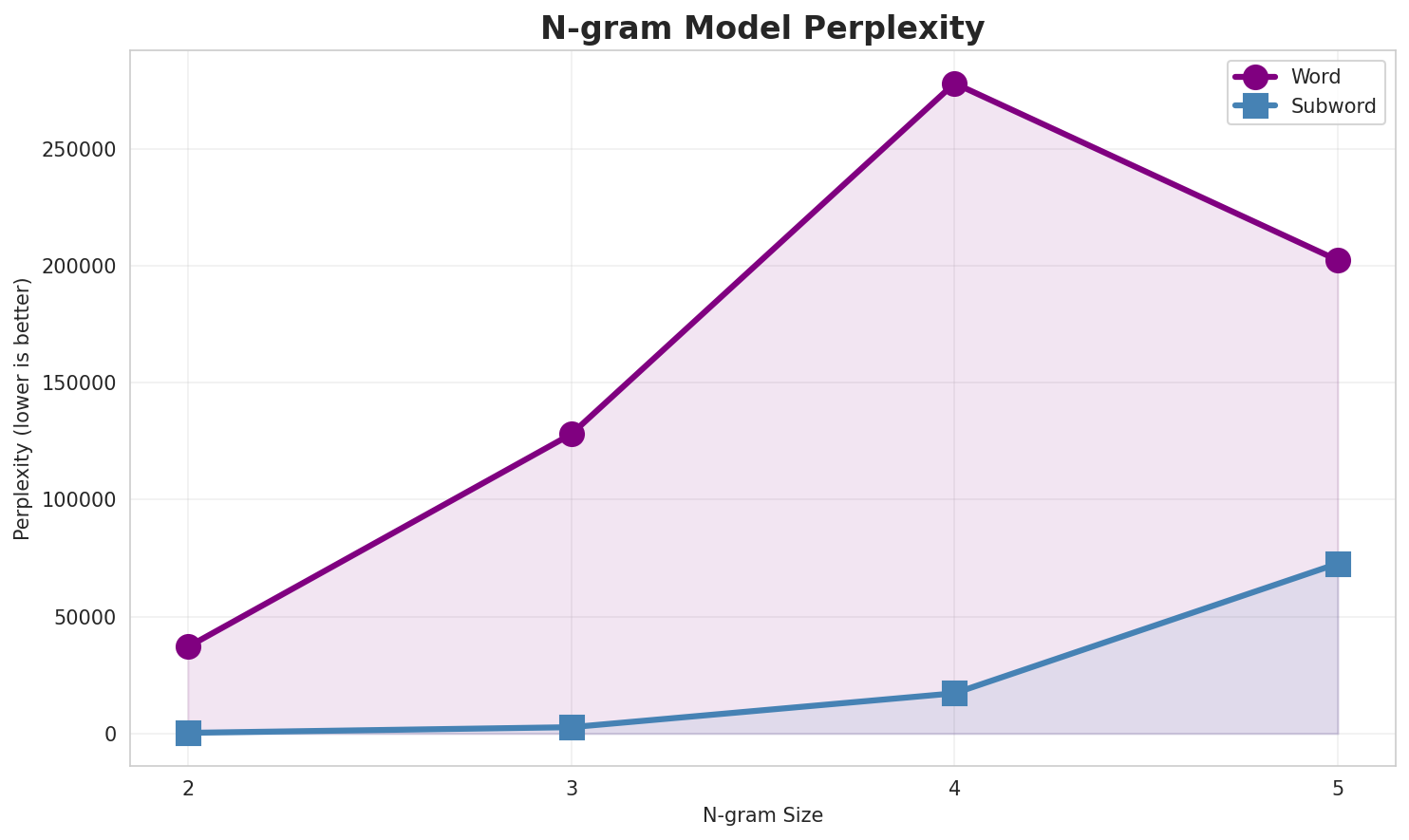
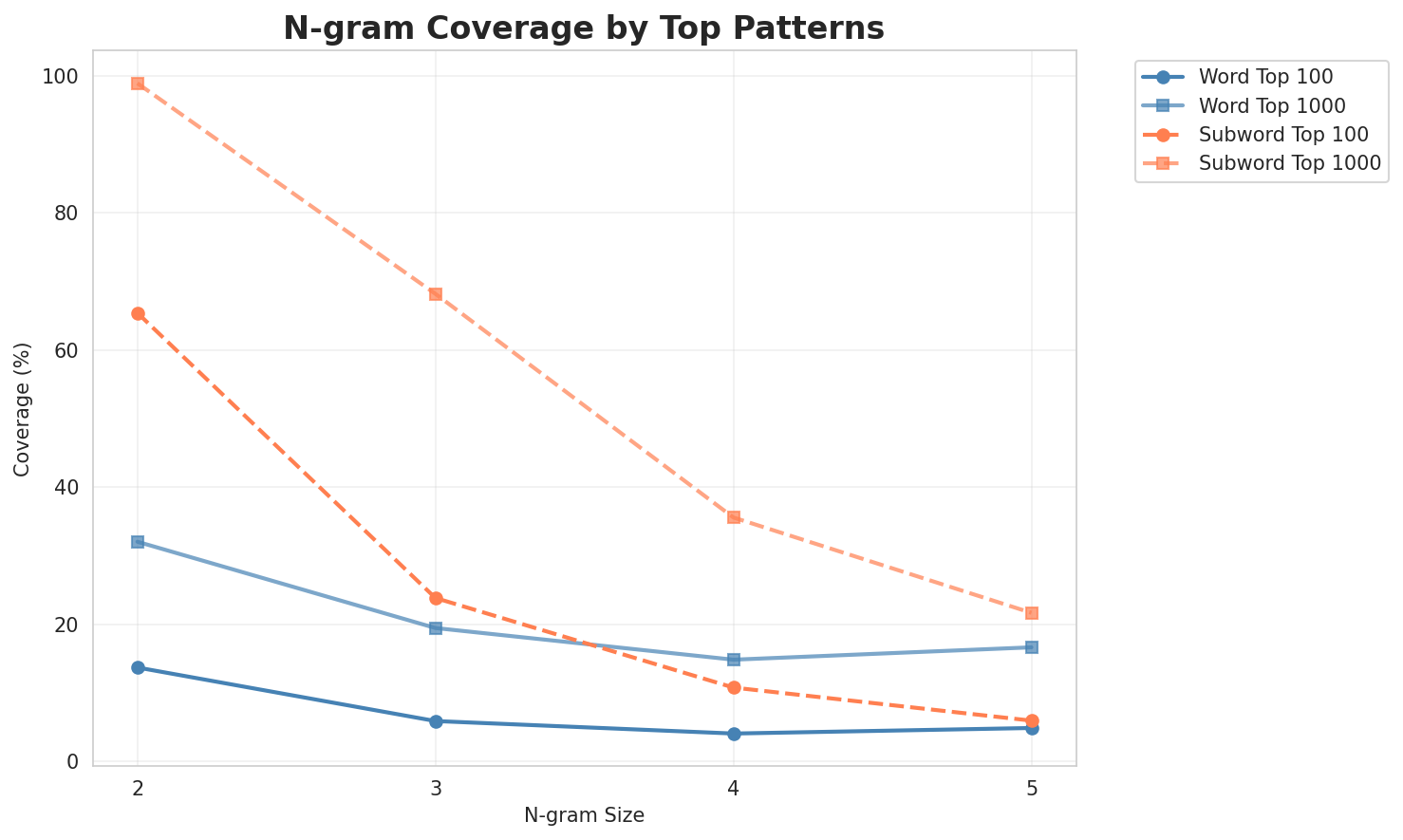
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
| N-gram | Variant | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | Word | 37,064 | 15.18 | 295,690 | 13.7% | 32.1% |
| 2-gram | Subword | 293 🏆 | 8.19 | 11,777 | 65.4% | 98.9% |
| 3-gram | Word | 127,942 | 16.97 | 571,162 | 5.9% | 19.5% |
| 3-gram | Subword | 2,712 | 11.41 | 80,865 | 23.9% | 68.2% |
| 4-gram | Word | 277,916 | 18.08 | 975,958 | 4.1% | 14.9% |
| 4-gram | Subword | 17,204 | 14.07 | 420,279 | 10.8% | 35.6% |
| 5-gram | Word | 202,294 | 17.63 | 684,204 | 4.9% | 16.7% |
| 5-gram | Subword | 72,650 | 16.15 | 1,308,264 | 6.0% | 21.7% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | e voe |
60,584 |
| 2 | ar c |
55,004 |
| 3 | a viz |
53,947 |
| 4 | e oa |
52,533 |
| 5 | d ar |
48,158 |
3-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | zo ur gumun |
17,679 |
| 2 | bro c hall |
15,683 |
| 3 | a zo ur |
15,380 |
| 4 | e oa bet |
13,023 |
| 5 | ur gumun eus |
8,893 |
4-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | zo ur gumun eus |
8,258 |
| 2 | monumantoù ha traoù heverk |
5,437 |
| 3 | a zo ur gumun |
5,065 |
| 4 | zo ur gumun e |
4,316 |
| 5 | monumant ar re varv |
3,982 |
5-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a zo ur gumun eus |
3,616 |
| 2 | ioc world bird list diwar |
2,760 |
| 3 | world bird list diwar benn |
2,760 |
| 4 | roadennoù ioc world bird list |
2,759 |
| 5 | zo ur gumun eus italia |
2,622 |
2-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ a |
1,908,238 |
| 2 | _ e |
1,681,083 |
| 3 | a n |
1,609,135 |
| 4 | e _ |
1,599,725 |
| 5 | r _ |
1,429,762 |
3-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a r _ |
641,927 |
| 2 | _ e _ |
641,853 |
| 3 | e t _ |
627,577 |
| 4 | _ a r |
556,810 |
| 5 | e n n |
468,710 |
4-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ a r _ |
457,578 |
| 2 | _ a n _ |
280,457 |
| 3 | a n t _ |
268,610 |
| 4 | _ g a n |
228,380 |
| 5 | _ h a _ |
223,259 |
5-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ g a n t |
202,257 |
| 2 | g a n t _ |
193,123 |
| 3 | _ h a g _ |
134,751 |
| 4 | _ e u s _ |
130,235 |
| 5 | e t _ e _ |
103,216 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram (subword) with 293
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~22% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
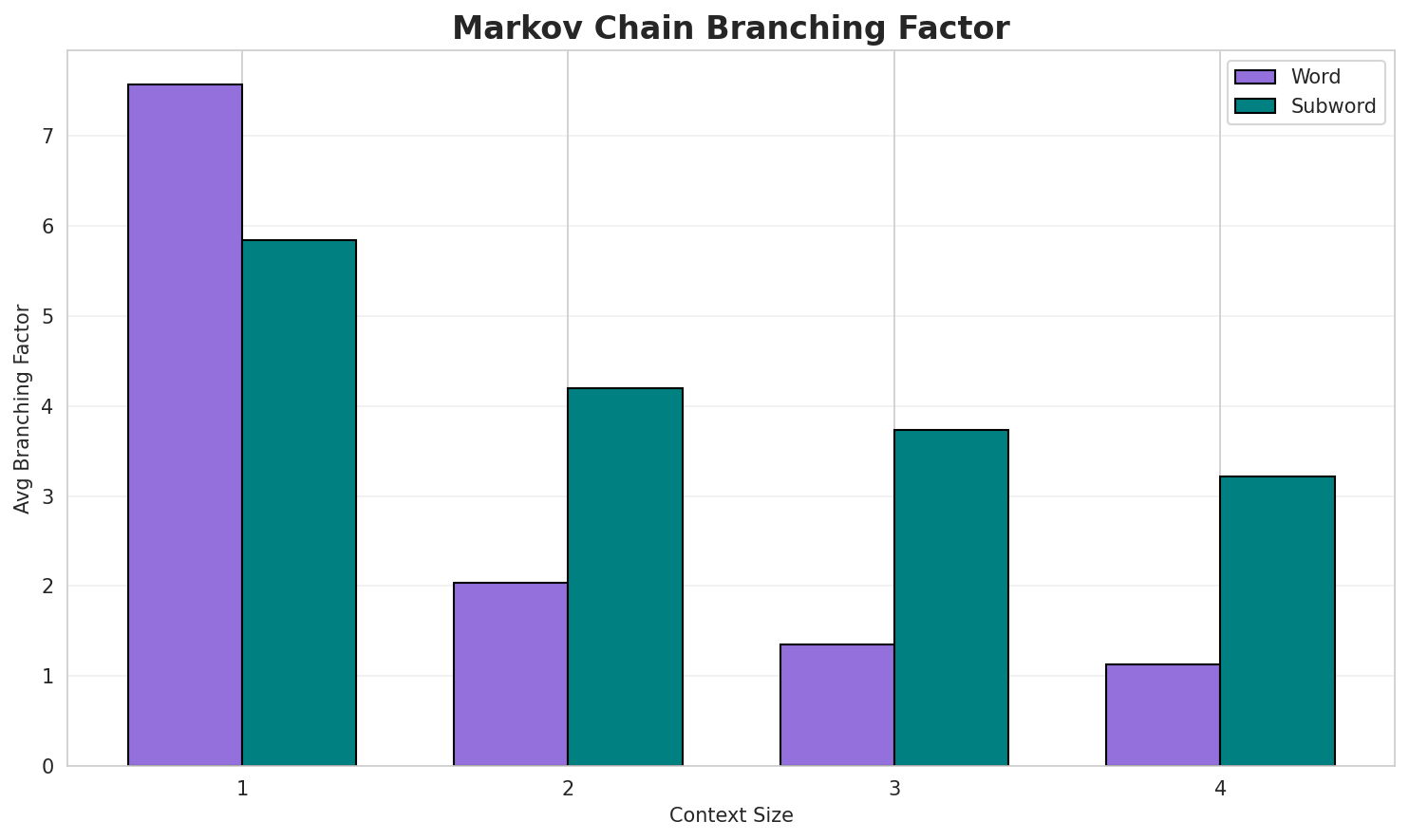
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
| Context | Variant | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Word | 0.8873 | 1.850 | 7.57 | 546,965 | 11.3% |
| 1 | Subword | 0.8951 | 1.860 | 5.84 | 8,419 | 10.5% |
| 2 | Word | 0.3297 | 1.257 | 2.04 | 4,120,028 | 67.0% |
| 2 | Subword | 0.6667 | 1.587 | 4.20 | 49,174 | 33.3% |
| 3 | Word | 0.1564 | 1.115 | 1.35 | 8,357,037 | 84.4% |
| 3 | Subword | 0.6634 | 1.584 | 3.73 | 206,424 | 33.7% |
| 4 | Word | 0.0731 🏆 | 1.052 | 1.13 | 11,199,579 | 92.7% |
| 4 | Subword | 0.6489 | 1.568 | 3.22 | 770,069 | 35.1% |
Generated Text Samples (Word-based)
Below are text samples generated from each word-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
e kastell aigneaux kantved merc h kannidi o devoa kemeret hent reter menezioù ezhomm da vontar boblañs melestradurezh tud ar pif gadget de carnac et seigneur isaac baron met breinet ganta ra eus bro c haokaz ar fedon ar 25vet rujumant troadegiezhfichenn hiniennel memorial genweb egile
Context Size 2:
e voe azoet an oferenn rak miret eo bet troet e galleg a 346 pajennad a zeuasar c haner en deus kumuniezhioù kumunioù beg ar skeul mañ zo levezonet gant friedrich dürrenmatt da viz eost e departamant il ha gwilen bro roazhon bet ganet d ar mare se e
Context Size 3:
zo ur gumun e spagn e kumuniezh valencia spagn pennadoù kar carlo ii charlez iañ karl iañ carloa zo ur sammad a stennadur a en em astenn a ra erv kourland eus ledenez sambia lecbro c hall société des amis de benjamin péret pour un second manifeste communiste gant grandizo muni...
Context Size 4:
zo ur gumun eus departamant calvados e bro c hall douaroniezh armerzh emdroadur ar boblañs melestrad...monumantoù ha traoù heverk iliz katolik sant albin ners douaroniezh emdroadur ar boblañs cassini hag...a zo ur gumun eus departamant pas de calais bro c hall istor armerzh kompagnunezh mengleuzioù bruay ...
Generated Text Samples (Subword-based)
Below are text samples generated from each subword-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
_cheunoù_wez:_beere_zharndütren_añs_t.lalel_da_k
Context Size 2:
_amm_da_gant_ges__evez._marezal_peannoù_art,_pag_ga
Context Size 3:
ar_senner._levelet_e_rout_-_bloarekuet_en_affarink_d’a
Context Size 4:
_ar_solinago,_mab_s_an_ilizoù_sir_kreiant_bet_kemeret_an_
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-4 (word) with 92.7% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (770,069 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 241,991 |
| Total Tokens | 15,343,130 |
| Mean Frequency | 63.40 |
| Median Frequency | 4 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 2509.84 |
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | e | 703,890 |
| 2 | ar | 518,682 |
| 3 | a | 468,243 |
| 4 | an | 326,691 |
| 5 | ha | 229,662 |
| 6 | gant | 189,178 |
| 7 | c | 187,433 |
| 8 | en | 180,997 |
| 9 | da | 171,218 |
| 10 | ur | 158,920 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | veyne | 2 |
| 2 | wga | 2 |
| 3 | codreanu | 2 |
| 4 | dumitru | 2 |
| 5 | maghrebonkoud | 2 |
| 6 | fidefide | 2 |
| 7 | ougandachess | 2 |
| 8 | cytonn | 2 |
| 9 | malinga | 2 |
| 10 | ablainville | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 1.1114 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.996756 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 41.9% |
| Top 1,000 | 65.8% |
| Top 5,000 | 80.5% |
| Top 10,000 | 85.7% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9968 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 41.9% of corpus
- Long Tail: 231,991 words needed for remaining 14.3% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
5.1 Cross-Lingual Alignment
5.2 Model Comparison
| Model | Dimension | Isotropy | Semantic Density | Alignment R@1 | Alignment R@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 32 | 0.8117 | 0.3810 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_64d | 64 | 0.8154 🏆 | 0.2792 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_128d | 128 | 0.8010 | 0.2076 | N/A | N/A |
| aligned_32d | 32 | 0.8117 | 0.3700 | 0.2440 | 0.6460 |
| aligned_64d | 64 | 0.8154 | 0.2752 | 0.3920 | 0.7600 |
| aligned_128d | 128 | 0.8010 | 0.2094 | 0.5340 | 0.8640 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: mono_64d with 0.8154 (more uniform distribution)
- Semantic Density: Average pairwise similarity of 0.2871. Lower values indicate better semantic separation.
- Alignment Quality: Aligned models achieve up to 53.4% R@1 in cross-lingual retrieval.
- Recommendation: 128d aligned for best cross-lingual performance
6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
This section presents an automated morphological analysis derived from the statistical divergence between word-level and subword-level models. By analyzing where subword predictability spikes and where word-level coverage fails, we can infer linguistic structures without supervised data.
6.1 Productivity & Complexity
| Metric | Value | Interpretation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Productivity Index | 5.000 | High morphological productivity | Reliable analysis |
| Idiomaticity Gap | -0.232 | Low formulaic content | - |
6.2 Affix Inventory (Productive Units)
These are the most productive prefixes and suffixes identified by sampling the vocabulary for global substitutability patterns. A unit is considered an affix if stripping it leaves a valid stem that appears in other contexts.
Productive Prefixes
| Prefix | Examples |
|---|
Productive Suffixes
| Suffix | Examples |
|---|---|
-s |
wolves, hobbs, cassis |
-où |
gwallzarvoudoù, emstummoù, pellgomzioù |
-us |
tarphonomus, benildus, gigantorhinus |
-er |
hompozer, siger, geschwister |
-es |
wolves, béssèges, fontenailles |
6.3 Bound Stems (Lexical Roots)
Bound stems are high-frequency subword units that are semantically cohesive but rarely appear as standalone words. These often correspond to the 'core' of a word that requires inflection or derivation to be valid.
| Stem | Cohesion | Substitutability | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
tion |
2.41x | 78 contexts | tione, eetion, motion |
adoù |
2.03x | 74 contexts | tadoù, padoù, hadoù |
emba |
2.26x | 40 contexts | emban, pemba, bemba |
iamm |
2.35x | 24 contexts | liamm, fiamma, fiamme |
ouar |
1.52x | 126 contexts | mouar, zouar, bouar |
nnet |
1.68x | 71 contexts | annet, rannet, rennet |
nnad |
1.53x | 98 contexts | mennad, gannad, vennad |
zhañ |
1.96x | 35 contexts | ezhañ, tizhañ, dizhañ |
reze |
1.52x | 94 contexts | rezet, dreze, breze |
ntañ |
1.75x | 51 contexts | antaño, vontañ, wintañ |
nnoù |
1.87x | 38 contexts | vannoù, gennoù, pennoù |
iwar |
2.55x | 13 contexts | diwar, ziwar, siward |
6.4 Affix Compatibility (Co-occurrence)
This table shows which prefixes and suffixes most frequently co-occur on the same stems, revealing the 'stacking' rules of the language's morphology.
No significant affix co-occurrences detected.
6.5 Recursive Morpheme Segmentation
Using Recursive Hierarchical Substitutability, we decompose complex words into their constituent morphemes. This approach handles nested affixes (e.g., prefix-prefix-root-suffix).
| Word | Suggested Split | Confidence | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|
| heureuses | heure-us-es |
6.0 | heure |
| burzhudoù | burzhud-où |
4.5 | burzhud |
| ziarbennoù | ziarbenn-où |
4.5 | ziarbenn |
| goudeskridoù | goudeskrid-où |
4.5 | goudeskrid |
| nijadegoù | nijadeg-où |
4.5 | nijadeg |
| ziskoulmoù | ziskoulm-où |
4.5 | ziskoulm |
| dasprenus | daspren-us |
4.5 | daspren |
| tradutores | tradutor-es |
4.5 | tradutor |
| drubuilhoù | drubuilh-où |
4.5 | drubuilh |
| reichsmarkoù | reichsmark-où |
4.5 | reichsmark |
| variantennoù | variantenn-où |
4.5 | variantenn |
| livuzennoù | livuzenn-où |
4.5 | livuzenn |
| kompozadoù | kompozad-où |
4.5 | kompozad |
| viñsaskelloù | viñsaskell-où |
4.5 | viñsaskell |
| kellennoù | kellenn-où |
4.5 | kellenn |
6.6 Linguistic Interpretation
Automated Insight: The language Breton shows high morphological productivity. The subword models are significantly more efficient than word models, suggesting a rich system of affixation or compounding.
7. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 64k BPE | Best compression (3.79x) |
| N-gram | 2-gram | Lowest perplexity (293) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (92.7%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.18073153},
publisher = {Zenodo},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
- 🤝 Sponsor: Featherless AI
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2026-01-03 20:37:28